Enzymes are Proteins: A Definitive Guide of 4000+ Words (Updated)
Enzymes are proteins that speed up the reactions by acting as catalysts. They increase the rate of reaction without being consumed or permanently altered by themselves. In Greek enzymes are divided into sections “En” which means “in” and second part is “zyme” means living. The study of enzymes is known as enzymology. (Enzyme Definition)
Physical nature of life is based on the making and breaking of different composed at all levels involved in the metabolism. Thousands of compounds must be shaped to produce the organelles and other structures present in living organisms. The formation may involve the making of large molecules from smaller molecules or vice versa, moreover all these reactions should take place at moderate temperature and with a speed good enough to support life. It is a common laboratory observation that reactions taking place within a cell if accomplished outside the cell needs very high temperature and there is no control on the speed of the reaction. Why the same reactions need different environments to accomplish when taking place inside the cell. What is the missing connection between living and non-living environment? Initially people thought that it is because of the life itself. A living thing can do what cannot be done by the non-living conditions.
History of Enzymes
The enzymes were first discovered by a French chemist named Anselme Payen. He named them as diastase in 1833. A few decades later, Louis Pasteur while studying the fermentation of sugar to alcohol by yeast discovered that there is an essential force, he called it ferments that only function within living organisms. The term enzyme was first used in 1878 by Wilhelm Kuhne, a German physiologist. Thus, after lot of hard work the scientists were able to find the missing connection. They were able to demonstrate that it is not the life but a large biomolecule made of amino acids, which behaves as a catalyst in the functioning of the cell. These large molecules not only speed up the reactions but also make them happen at moderate temperature which can support life. This biomolecule takes part in all the formations and breakdown of compounds which follow specific pathways.
All the reactions require the biomolecule as definite controlling system. The control should be for the direction, speed and specificity of the undergoing reaction. Cells control all operations by producing the proper biomolecuse, named Enzymes. The enzymes are proteins that always produced in the proper amounts, at the proper time and the proper place where they are needed and according to research their are different factors that affect enzyme activity i.e., pH, Temperature, Enzyme and Substrate Concentration etc.
As mentioned above in the enzymes definition, they are required by the biomolecules, because nearly all chemical reactions of life are so slow without catalysts that they cannot sustain life. The enzymes generally speed up reaction rates by factors between 108 and 1020 and thus made the life process possible.
Structure of Enzymes
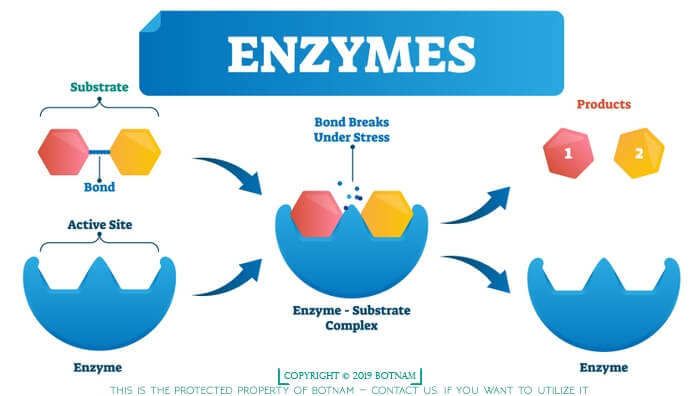
One of the basic qualities of enzymes is that they are specific in action. If we elaborate the specificity, we will understand that specificity is because of their power of recognizing the substrate from a sea of molecules. How they do this. They do this because of the specific structure of the substrate. This means that enzymes are structure specific in nature. This structure specificity of the enzymes is based on their own specific structure when proper substrate colloids with a proper enzyme having proper structure, they fit in to carry out the phenomena of catalysis. Thus, for the proper understanding of Enzymes and enzyme action we need to understand their structure and chemical nature.